Companies
Growing concern over school milk program
Updated: 2011-04-28 09:28
By Zhou Wenting (China Daily)
|
 |
|
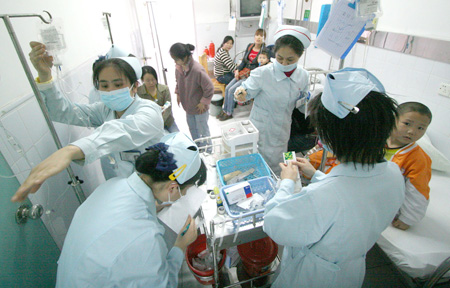
Kindergartners in Zhuhai, Guangdong province, are treated in March 2008 after drinking contaminated milk. The company that provided the milk was not qualified for the school milk program but was a longtime supplier. [Photo / China Daily] |
Health scares continue to damage public confidence, reports Zhou Wenting in Beijing.
A national school milk program intended to improve children's health has soured again.
On Friday morning, 251 children at Yuhe Town Central Primary School in Yulin, Shaanxi province, fell ill after drinking school milk produced by the Mengniu Dairy Group. They were sent to hospital for treatment, and were all discharged by the following day.
|
||||
The tests were conducted by Yulin's Center for Disease Control and Prevention and the results were announced by the city's food safety committee.
On Tuesday evening, Mengniu said on its website that it would work with the school and the local health department to track the students' health. But public confidence in China's developing school milk program suffered another blow.
Dairy enterprises are impaired by suspected and real poisoning incidents and low profits. Schools stay out of the program because they do not want to be implicated in safety scandals. And the country has no unified management or supervision of the program it started in 2000.
Milk producers and local watchdogs are the first to be blamed for bad quality control, but experts also have doubts about the guiding theory behind the program.
Two tests, two results
Mengniu breathed a corporate sigh of relief at the test report, but food safety experts didn't let it go easily.
"Why do accidents always happen at branch plants?" said Sang Liwei, a food-safety lawyer in Beijing and a representative of the Global Food Safety Forum, a non-governmental organization.
The milk the Yulin children drank was processed at a local plant in Baoji that is owned by Inner Mongolia-based Mengniu. "One month ago," Sang said, "milk withdrawn from circulation was also produced by a subsidiary plant", that one in Zhengzhou, Henan province, and owned by Shanghai Bright Dairy & Food.
Mengniu was involved in two milk incidents in Shaanxi province within the past year, but test results for both set it free. Experts called for a new test by higher authorities.
Sang mentioned safety concerns at Nongfu Spring in Haikou, Hainan province, in 2009. Haikou Municipal Industrial and Commercial Bureau detected excessive mercury in the drinking water, but a later test by the provincial bureau showed the water met standards.
"No matter what happened behind the scenes, it at least showed that two tests can give different answers," Sang said.
Food safety experts said if the questioned milk indeed passed the tests, then the standard for dairy products in China is doubtful.
"We have two tests: qualitative and quantitative," Sang said. "Sanlu's baby formula had also been qualified before 2008, because there wasn't a test target for melamine," Sang said.
An estimated 300,000 infants, including six who died from kidney stones or other kidney damage, became victims of baby formula produced by Sanlu Group Co in 2008. The chemical melamine, which was added to the milk, caused it to appear to have a higher protein content.
So what really caused the Yulin schoolchildren to become ill?
Hours after the test results were announced, Mengniu suggested two possible reasons - the "unscientific" way the children drank the milk and hysteria, because "only 16 students vomited and felt nausea at first".
"After drinking the cold milk on an empty belly, some students experienced upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and other symptoms of gastritis," said Zhao Yuanhua, vice-president of Mengniu Dairy Group.
Specials

British Royal Wedding
Full coverage of the royal wedding of Prince William and Kate Middleton in London. Best wishes

The final frontier
Xinjiang is a mysterious land of extremes that never falls to fascinate.

Bridging the gap
Tsinghua University attracts a cohort of foreign students wanting to come to China.



