 |
|
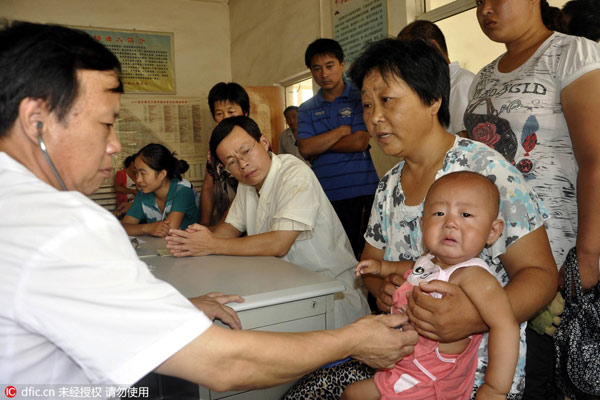
A doctor sees a young patient in a clinic in Chiping county in Liaocheng city, East China's Shandong province. [Photo/IC]
|
Had the long-awaited two-child policy not been announced at the end of last year, the severe shortage of pediatricians in China would probably have not attracted public attention. The irony is that the most populous nation is running short of not only babies, but also physicians to attend babies. While long queues and big crowds in Chinese public hospitals are not new, those in pediatric departments can be even more appalling. Waiting overnight just to register an ill child is fairly common experience for anxious parents and grandparents. Now, the expected baby boom and anticipated growing demand for child and maternal care have prompted medical policymakers to pay serious attention to the issue.
The weak capacity of pediatric departments in China is complex and multifaceted. First, the philosophy of medical education prevalent in the late 1990s somehow preferred general medical training over specialized pediatric training, compounded by the perceived declining demand because of low birth rate. And starting from 1999, many medical schools stopped offering undergraduate programs in pediatrics.
Postgraduate education alone has not been able to train enough pediatricians. In stark contrast to the mounting needs, the number of pediatricians in China has actually dropped. For every 10,000 children under 14, China has just 5.3 pediatricians, a figure much lower than the international standard. Estimates suggest 200,000 more physicians are needed to fill up the personnel gap in pediatric departments.
Second, growing demand and shrinking supply combine to mean heavy workload for physicians. The average outpatient load for pediatricians is 2.6 times heavier than other specialist physicians. It is not uncommon for those in major tertiary hospitals to attend more than 100 children a day while putting in more than 20 hours of overtime a week. Many studies have reported severe burnout syndrome and occupational stress of Chinese pediatricians, leaving this profession often the last choice when medical graduates choose their specialties.


 Stars of Lijiang River: Elderly brothers with white beards
Stars of Lijiang River: Elderly brothers with white beards
 Wealthy Chinese children paying money to learn British manners
Wealthy Chinese children paying money to learn British manners
 Military-style wedding: Fighter jets, grooms in dashing uniforms
Military-style wedding: Fighter jets, grooms in dashing uniforms
 Striking photos around the world: May 16 - May 22
Striking photos around the world: May 16 - May 22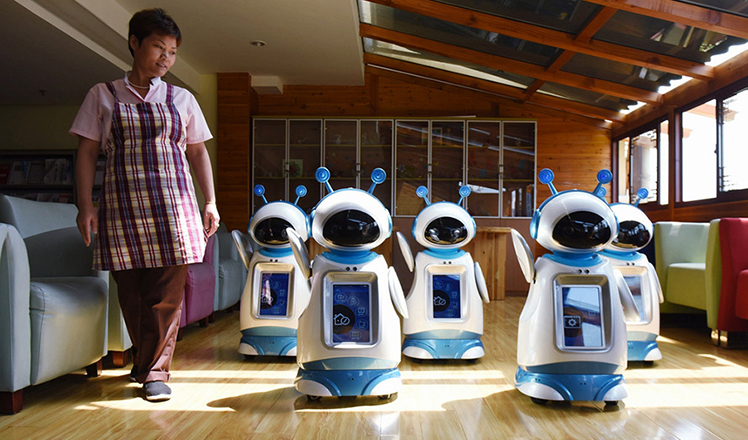
 Robots help elderly in nursing home in east China
Robots help elderly in nursing home in east China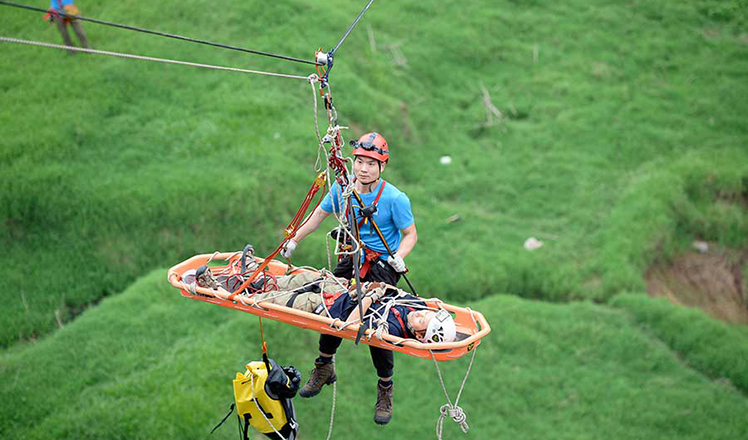
 Hanging in the air: Chongqing holds rescue drill
Hanging in the air: Chongqing holds rescue drill
 2.1-ton tofu finishes in two hours in central China
2.1-ton tofu finishes in two hours in central China
 Six things you may not know about Grain Buds
Six things you may not know about Grain Buds














