How a desert branched out to become Beijing's guardian
 |
|
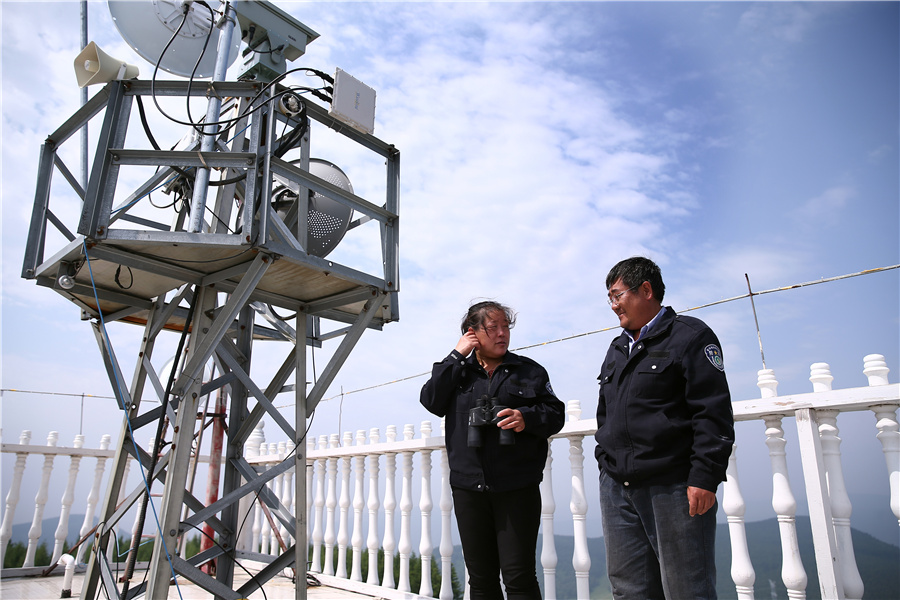
Liu Jun and his wife, Qi Shuyan, on the roof of their watchtower in Saihanba. [Photo by Zou Hong/China Daily] |
Isolated for months at a time in an ocean of greenery
Liu Jun's most-treasured possession is a pair of binoculars. For the past 12 years, he has carried them with him almost wherever he goes. During spring and autumn, the fireprone seasons, he picks them up once every 15 minutes during daylight and once an hour at night.
Through the binoculars' lenses, the color green fills Liu's eyes. Scanning the expansive woodland, he keeps a watch for the slightest hint of smoke that could wreak havoc.
Liu is a fire watcher. His job is to keep an eye out to ensure that any smoke that comes into his field of vision does not become a forest fire.
His workplace, a 16-meter-high tower atop the highest peak in Saihanba National Forest Park, Hebei province, stands at an altitude of 1,940 meters above sea level. The nonstop howling wind provides a contrast to the forest, which resembles a gigantic clump of emerald.
The wind is more bearable than the cold, though. Throughout the year, the average temperature is about -1.3 C, but in the depths of winter it can drop as low as-44 C.
Though the climate is a problem today, it was even worse before the early 2000s because there was no electricity supply.
"Every October, before winter came, the people who manned the watchtower would store plenty of firewood, which they found on the mountain, and relied on it for the next six months," said Liu, 46, whose suntanned face and unkempt hair make him appear older than his years.
"Despite the firewood, the place was still as cold as a huge icebox. The fire watchers had to scrape at the frost-covered windows to peer outside."
The stories of his predecessors still haunt him. When the watchtower was built in 1962, it wasn't really a tower, but a humble shed propped up on tree trunks and covered with straw.
Today, the only reminder is a black-and-white photo hanging on the wall along the stairs in the new watchtower. The image sits alongside color photos of the second-and third-generation towers-both brick constructions resembling building blocks.
Liu is the fourth-generation of fire watchers, and his L-shaped, five-story building with a climbable roof finally merits the designation "tower". The forest has nine, including Liu's.
"Here, not a single winter passes without heavy snowfall, so heavy that all the roads down the mountain are blocked," he said.
In the old days, especially during the 1960s and '70s, the snow forced the tower's occupants to stay there for the entire winter.
"Throughout that time, they had nothing to drink but snow water and nothing to eat but dried pickles and frozen steamed flour buns as hard as stone. The water smelled strongly of tree sap," he said.
"Some tried raising animals to provide themselves with some desperately needed company," Liu said. "But it was hard. Although there were cases where geese had weathered through the winter before giving birth to goslings in spring, in other cases, rabbits lost their long ears to the biting cold."
When wild animals, such as boars and skunks came "knocking on the door" at night, they were simply driven away and rarely harmed. "Their visits, although a little scary, were appreciated during the long winter nights filled with the howls of snowstorms," Liu said.
Tragedies occurred, too.
A husband-and-wife team, Chen Ruijun and Chu Jingmei, were also firewatchers. One Spring Festival-which usually falls in January or February-they decided that one of them would go home to see their daughter, while the other would stay at their watchtower.
Chen, the husband, stayed. But a few days after Chu left, he caught a bad cold. He lay down, and was unable to lift himself up when the illness took hold. He felt nailed to his bed, with no energy left. Gradually he lost consciousness.
When he eventually opened his eyes, Chen saw a stout man looking at him intently, his broad hands holding his own. The man was a local farmer who had lost his horse, and his search had taken him to Chen's watchtower. His unexpected arrival helped save Chen's life.
That was in the mid-1980s. Chen died in 2011, at age 54. The watchtower he once occupied was demolished in the 1990s to make way for the construction of a new one, which in turn was replaced in 2014 by the one Liu and his wife now occupy.
Electricity became available in the early 2000s, but there was no hot water until three years ago.
"Before, I had to go for weeks or months without taking a shower," said Liu, who used to travel long distances to fetch water from rivers, and climb the mountain slope with packages weighing 100 kg on his back containing several months' food.
One thing that hasn't changed in the past 55 years is something Liu has in common with every firewatcher who has worked at Saihanba: loneliness. "The feeling of isolation is enough to break a man who thinks nothing of the cold and hardship for which the area is renowned," he said.
"After being locked in the tower for two months, I thought I was going mad," he said. "I wanted to be out there digging holes and planting trees. It was tough work, but at least you got to see people."