Taking customers to a Haier ground to serve them better
Updated: 2013-10-01 14:31
By Cecily Liu in London (China Daily)
|
||||||||
|
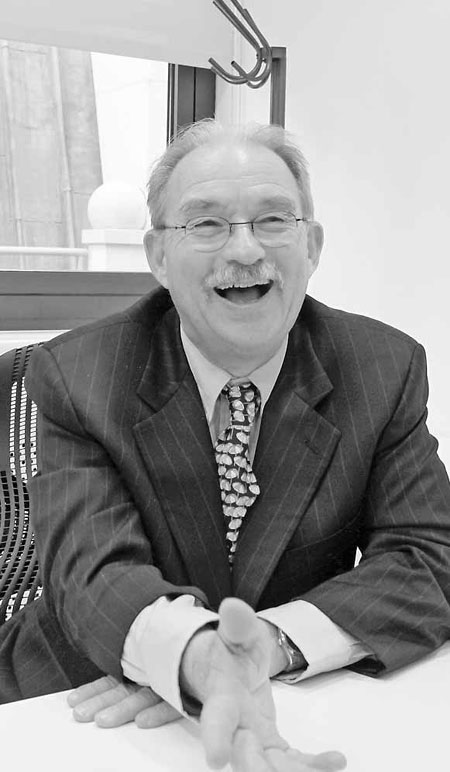
Bill Fischer says what distinguishes Haier is an ability to learn new lessons. Cecily Liu / China Daily |

Expert sees the innovative home appliance company leading the way
Courageous managers who turn employees into entrepreneurs will help China create a knowledge economy, says Bill Fischer, professor of innovation management at Switzerland's IMD business school.
Fischer, 67, who is also course director of an IMD-Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business joint program, says such a corporate structure is key to ensuring responsiveness to customers' needs in big companies.
"As China's low labor advantage diminishes, it is critical for China to focus on growing its service sector, for which flexibility and zero distance from the customer is key to success," he says.
A prime example of this is the Chinese home appliances manufacturer Haier, which Fischer studied with researchers Umberto Lago and Fang Liu for a book published earlier this year.
Reinventing Giants: How Chinese global competitor Haier has changed the way big companies transform traces Haier's rise from a low-quality manufacturer to an innovative and service-oriented brand over the past 30 years.
A key innovation of Haier's management structure is inverting the traditional relationship triangle - where managers are at the top, followed by middle management, then a sales team and finally customers - to one that positions customers at the top.
In the new structure, the customers' needs are learnt by the sales team and fed back to Haier's top managers, who make decisions about the company's strategies based on this information. The role of middle management is taken out of the model.
"Once customers are at the top, why do you need middle management? Is it to manage the top managers?" Fischer asks. "No. Many companies in the world say that they put customers first without knowing what it means. But Haier has executed it well."
At Haier, the company's management structure pivots around ZZJYTs (zi zhu jing ying ti, which in English means independent operation units).
Each new project or market opportunity leads to the formation of a ZZJYT, a dedicated small team of workers with a separate budget, functioning almost like an independent company.
Fischer and his co-authors studied Haier's three-door- refrigerator ZZJYT in detail. First a leader is selected who is then responsible for recruiting the team.
The ZZJYT model inspires entrepreneurial spirit in workers, Fischer says. It gives them decision-making power and motivation to work hard because their salary is directly related to the performance of the unit.
The key benefit of the ZZJYT arrangement is fast response to customer needs, he says, but such a structure requires courage by a company's top management to implement it.
To truly comprehend Haier's daring and innovation, one needs to understand the state of China's home appliances industry in 1984, when Haier was founded, Fischer says.
"Back in the early 1980s, there were no refrigerators in China. To store vegetables, you would dig a hole in the ground and bury them. When you needed your greens, you dug up the cabbages, washed them and cooked them."
"In 1984, refrigerators started to become available, but they were very hard to get because the supply was still very scarce. You would get people standing on the roads outside department stores with renminbi in their hands bidding to buy refrigerators."
There was no quality assurance, he says, no such thing as customer service. Those who could buy broken refrigerators would consider themselves lucky, because they could fix them.
"But Haier's CEO Zhang Ruimin knew this would not last. He said, 'Some day, China will be a developed market. We need to be in a position where we have brand differentiation'," Fischer says.
In 1985, when a customer returned a refrigerator to Haier for quality reasons, Zhang and the customer went through an entire inventory of 400 refrigerators looking for a replacement. In the process, he discovered that 20 percent of his goods were of unacceptable quality, Fischer says.
Zhang then instructed 76 employees to smash 76 substandard refrigerators in the street outside the Haier factory to publicly demonstrate the company's quest for quality.
"Zhang made a bet that there would be people willing to pay a premium for quality products in the future, so he worked on introducing a quality product ahead of such market demand," Fischer says.
Haier went on to introduce a new reward system for employees, where their output is evaluated daily. Managers attributed each task to a specific person, so mistakes were also quickly identified, rectified and penalized.
This model helped Haier to achieve quality for refrigerators, but, several years later, when its competitors caught up, it moved ahead again by creating a service-oriented strategy.
"By this time, Zhang said that Haier needed to become more responsive to customer needs. He did it by building market chains," Fischer says.
Each department within the company became the customer of the next department along the supply chain, the pooled feedback helping the company focus on the needs of the end buyers.
The design department, for instance, would be the customer of the environmental testing laboratory; the product divisions became customers of the technical facilities department; managers and employees were the customers of Haier's staff training unit.
This happened in the 1990s, Fischer notes, and come the turn of the century, Haier and Zhang's thinking again had a jump on the market. He proposed the concept of "zero distance to the customer" so the ZZJYT units were created.
Fischer says the story of Haier fascinates him, and counters the stereotypical view that Chinese products are cheap and of low quality.
Now he is researching more Chinese companies to better understand the connection between innovative management techniques and China's business environment and cultural influences.
Another project that will soon bring him closer to Chinese business leaders is the China Strategy Challenge, a four-day program next month organized by IMD and China's Cheung Kong Graduate School of Business.
It will take place at IMD's campus in Lausanne and be attended by both Chinese and European entrepreneurs, who, it is hoped, will learn lessons from each other through group activities.
Fischer says learning from European counterparts is an important step for Chinese entrepreneurs to turn their companies into global industry leaders. Even Haier has something to learn.
"Haier is an industry leader today, but it has to continue to transform itself to become a leader tomorrow," he says. "Haier's advantage is its ability to learn new lessons."
Zhang, he says, had two ideas that helped Haier's success - the determination to serve customers better, and empowering employees by giving them more independence.
cecily.liu@chinadaily.com.cn
(China Daily USA 10/01/2013 page16)
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
US government partial shutdown begins
Pentagon reassures China over India ties
China committed to deepening reform
Chinese embassy in Syria attacked
Li: China confident in meeting economic targets
New FTZ gets a big US bank
China, India join hands on border stability
China issues guidance for government purchases
US Weekly

|

|