The role of media vis-a-vis crimes
Updated: 2013-08-05 09:39
By Patrick Mattimore (China Daily)
|
||||||||
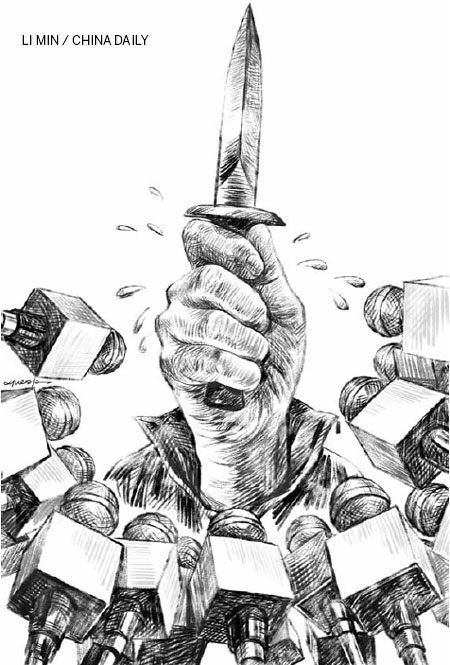

The recent spate of stabbings in China raises an interesting psychological question and media dilemma quite apart from the tragic events themselves. Has detailed media exposure of the crimes exacerbated the problem, resulting in copycat acts, thereby further disturbing social security? If so, does the media have a responsibility to report such incidents in a manner that mitigates the likelihood of the acts being repeated?
Before attempting to address the questions, there is an important caveat to consider: Have stabbings actually increased in China in recent weeks? That seems to have a self-evident answer, because the stabbings have been more in the news. But without a statistical breakdown, it is impossible to know whether stabbings or merely reports on them have increased.
For example, three years ago the media reported that there was an "epidemic" of suicides at the electronic company Foxconn. For months, the press reported each of the gruesome suicides in detail. A host of news reports appeared to suggest that the company was at fault and needed to change its policies. It turned out, however, that Foxconn's suicide rate during that particular reporting cycle was actually lower than China's national average based on the number of employees working at Foxconn.
If, after a thorough investigation, journalists discover that the stabbings in recent weeks have increased, then psychology may have a few answers as to why. But even those answers should be taken with a grain of salt, since it is always easier to offer ex post facto explanations for phenomenon than to predict future behaviors or events.
While it is not altogether clear why an individual will imitate another's criminal behavior, it is a well-established psychological principle that we do model our behavior according to what we see others doing.
Beginning with an ingenious experiment in 1961, Stanford University psychologist Albert Bandura helped social learning theorists recognize that individuals can learn merely by observing the behaviors of others.
In Bandura's Bobo doll experiment, children watched a television monitor in which adults punched and kicked a 5-foot plastic blow-up doll. When the children subsequently were in a room with the Bobo doll, they imitated the adults' aggressive behavior, thus providing evidence that learning occurs through modeling. Bandura also found that children who were not exposed to the aggressive model were unlikely to behave aggressively.
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
China's obesity rate on the increase
Washington Post sold to Amazon's founder
Fonterra says sorry for 'anxiety'
Detroit Symphony brings China to NYC
Service sector drives up growth
Globalization of Chinese culture becomes hot topic
Huawei expands in London
Web 'answer to export woes'
US Weekly

|

|