Price fall dims inflation
Updated: 2013-06-24 10:39
(bjreview.com.cn)
|
||||||||
The drop in bulk commodity prices signifies a shift in the direction of the Chinese economy
Considered a "weathervane" for the state of the economy, the prices of bulk commodities in China have been on decline since the second half of 2012 and show no signs of a turnaround.
|
 |
|
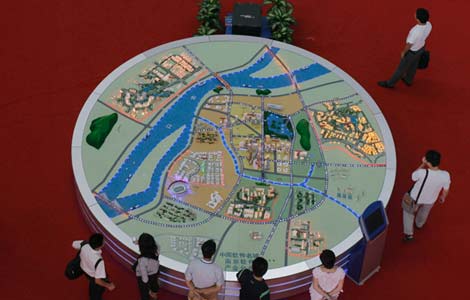
Workers operate a machine to lift rolled steel at a steel market in Shijiangzhuang, capital of north China's Heibei province, on April 2. |
According to the Mysteel Bulk Commodity Price Index of China (MyBCIC), in May the index stood at 1,060.65, a year-on-year decline of 8.3 percent and a drop of 1 percent on a monthly basis. What follows the declining index is sluggish economic growth.
The fall in bulk commodity prices, which serve as materials for industrial production, is pulling down the producer price index (PPI). According to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), in May the PPI dropped by 2.9 percent from a year ago, the lowest within the past eight months. On a monthly basis, the index declined by 0.6 percent. In the January-May period, the PPI dropped by 2.1 percent year on year.
Jiang Shengli, chief analyst on bonds and the macroeconomy with Haitong Securities Co Ltd, says the PPI has kept falling for 15 months, and the trend will soon affect retail prices. In May, the growth of consumer price index stood at 2.1 percent, lower than market expectations. Jiang says the price fall in the production sector rouses concern in the market. It indicates that production capacity is excessive and market demand is inadequate.
Investment has also been declining. According to the NBS, in the first five months of the year, growth in fixed assets investment was 0.2 percentage points lower than growth in the first four months, and private investment growth dropped by 0.1 percentage point over a year ago. Both private and State-owned capital has become less enthusiastic about making investments.
Such pessimism has spread to international financial institutions. On June 14, Morgan Stanley cut China's 2013 GDP growth forecast from 8.2 percent to 7.6 percent, following similar predications by the United Bank of Switzerland and Barclays Bank.
Hu Yuyue, a professor with the Beijing Technology and Business University, thinks China's bulk commodity prices will continue to fall, and with that the Chinese economy will unlikely resume double-digit growth.
The public should not worry about sluggish economic growth reflected in the fall of commodity prices, says Hu, because the drop has a positive side: Consumers, suffering from the pains of previous price hikes, can breathe a sigh of relief.
End of an era
During the 12 years since China's accession to the WTO, bulk commodity prices on the global market have risen rapidly while the Chinese economy has also witnessed rapid growth. During this period, China's demand for commodities accounted for 70 percent of the world's total, and its thirst for iron ore and coal accounted for 80 percent. Although China has become the biggest buyer of bulk commodities, it holds no pricing power because the market belongs to sellers.
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
Xi vows bigger stride in space exploration
US 'stole' China's statistics
Mandela's condition critical
Suspect in shooting spree detained
Mountaineers killed in Pakistan
Foreign firms eye new 'opening-up'
Project halted due to bird nests
Man gets death for killing 7 in 9 days
US Weekly

|

|