One year of clearing the air to greet another
Updated: 2015-12-23 08:07
By Han Xiaoping(China Daily)
|
||||||||
 |
|
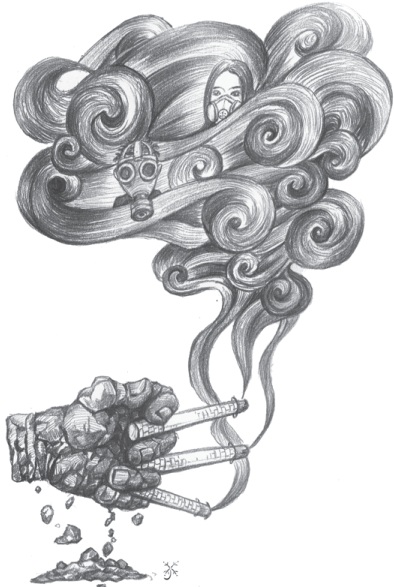
MA XUEJING/CHINA DAILY |
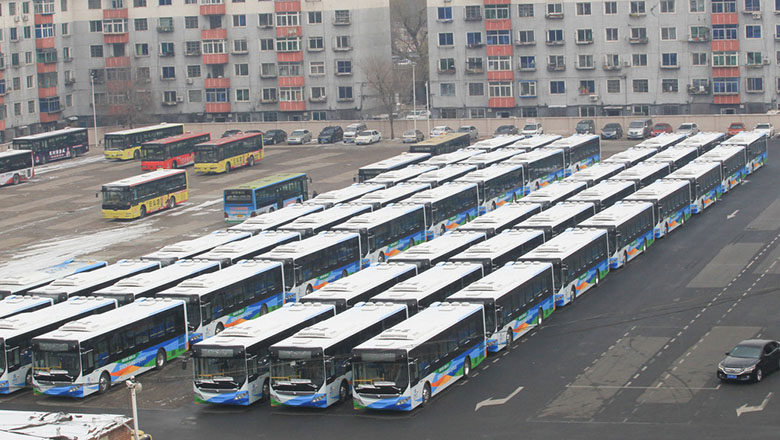
Beijing has issued two red alerts against air pollution in two weeks. This signifies heavier pollution, but it also shows that the authorities have become more vigilant to air pollution. Seen together with the other measures it has taken, we can say the Beijing municipal government has been more determined in 2015 to curb air pollution.
Opinions on the root causes of air pollution in China differ, but there are some common factors. Burning of coal is the first. China still burns coal to generate about 70 percent of its electricity and its annual coal consumption is more than 4 billion tons.
Earlier this month, the Chinese government announced on its official website a plan to improve technologies and reduce the ratio of coal in power generation to less than 310 grams per kilowatt hour. The plan will hopefully save 100 million tons of coal a year by 2020 and, along with other measures to reduce the reliance on coal, greatly improve the air quality.
The second problem is the poor quality of petroleum we use because China does not get the supply of good quality oil and its processing plants are not that efficient. The petroleum used in China has quite a high percentage of aromatic hydrocarbons.
Way back in the 1990s, the then ministry of chemical industries had said it feared that the use of such oil would release more particulates into the air. That fear has come true, as can be seen from the smog over large parts of North China for the past few years.
The key to solving this problem lies in introducing new-energy automobiles and encouraging people to use electric or hybrid cars. The government is already promoting such vehicles, for which it had set up more than 40,000 charging posts in some major cities by September - and has vowed to build more.
Besides, municipal governments should try to replace buses running on fossil fuels with those that operate on natural gas, because natural gas emits less greenhouse gases and particulates, and is abundant in China.
The third problem is related to agricultural areas. After harvest, farmers in China burn millions of tons of straw each year because it is the easiest way to dispose of them. And straw burning is an important cause of the smog that envelops North China in autumn and winter. To prevent the burning of straw, therefore, the State should buy the agricultural byproduct along with the grains and sell it to companies producing methane gas, which can replace coal as fuel in rural areas.
The authorities know the causes of air pollution and have taken measures to treat them. But more needs to be done. For example, as oil prices continue to fall, more Chinese people are buying cars and using more fossil fuels. In 2014 alone, more than 4.1 million SUVs were sold in China - compared with only 1.7 million in the United States - and the number is expected to cross 5 million this year.
The government has no choice but to adjust the oil price mechanism to dissuade people from buying cars that guzzle oil. Car owners may oppose such a move, but they should realize that the health of the population is more important than the comfort of a few.
That air doesn't have any boundaries and the air quality in Beijing cannot be improved in isolation should be made clear to all. For instance, despite shutting down its last coal-powered power plant in May 2013, Beijing has not seen much improvement in its air quality because the many high-polluting plants in neighboring Hebei province have been spreading toxic smoke in all directions.
Given these facts, the authorities are likely to take two new measures in 2016. First, they could strengthen coordination among Beijing, Hebei and Tianjin municipality, so that the whole of North China can fight smog together. And second, they might invest more in energy-saving technologies and new energy industries. These measures are both necessary and urgent because we cannot let the air quality worsen any further in the new year.
The author is chief information officer of China5e.com, an energy information website.
- Global health entering new era: WHO chief
- Brazil's planning minister steps aside after recordings revelation
- Vietnam, US adopt joint statement on advancing comprehensive partnership
- European border closures 'inhumane': UN refugee agency
- Japan's foreign minister calls A-bombings extremely regrettable
- Fukushima impact unprecedented for oceans: US expert

 Stars of Lijiang River: Elderly brothers with white beards
Stars of Lijiang River: Elderly brothers with white beards
 Wealthy Chinese children paying money to learn British manners
Wealthy Chinese children paying money to learn British manners
 Military-style wedding: Fighter jets, grooms in dashing uniforms
Military-style wedding: Fighter jets, grooms in dashing uniforms
 Striking photos around the world: May 16 - May 22
Striking photos around the world: May 16 - May 22
 Robots help elderly in nursing home in east China
Robots help elderly in nursing home in east China
 Hanging in the air: Chongqing holds rescue drill
Hanging in the air: Chongqing holds rescue drill
 2.1-ton tofu finishes in two hours in central China
2.1-ton tofu finishes in two hours in central China
 Six things you may not know about Grain Buds
Six things you may not know about Grain Buds
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
Liang avoids jail in shooting death
China's finance minister addresses ratings downgrade
Duke alumni visit Chinese Embassy
Marriott unlikely to top Anbang offer for Starwood: Observers
Chinese biopharma debuts on Nasdaq
What ends Jeb Bush's White House hopes
Investigation for Nicolas's campaign
Will US-ASEAN meeting be good for region?
US Weekly

|

|








