Former military base opens doors
Updated: 2013-06-03 07:37
By Cui Jia and Mao Weihua (China Daily)
|
||||||||
One-time nuclear testing ground is still little known, report Cui Jia and Mao Weihua in Bayingolin Mongol autonomous prefecture.
Editor's note: This is the eighth in a regular series of reports brought together under the banner "Lost Horizons", which aim to show life in the less-reported areas of the country and to give a voice to those whose words often go unheard. Slideshows and video footage are also available at www.chinadaily.com.cn/video
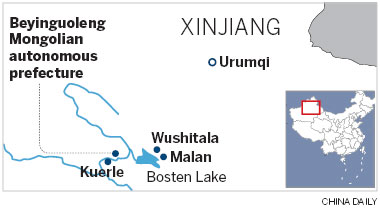
Wushitala township in the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region is only able to thrive because it is next to the Malan military base.
The township's businesses, such as grocery stores, as well as fruit and vegetable markets, are hives of activity. They buzz with military personnel and curious tourists excited to be near the mysterious and legendary military base - which goes unmarked on maps - where China's first nuclear and hydrogen bombs were tested.
The base remains, but the testing center closed many years ago.
The soldiers and their relatives visit the small restaurants that specialize in cuisine from provinces such as Shaanxi, Sichuan, Shandong and Henan to enjoy a taste of hometown cooking.
A local legend in Wushitala, which means "horse orchid" in the Uygur language, says the center's first commanding officer named the base after the profusion of flowers he saw growing across the moonlike sands of the Gobi desert.
"Horse orchid" is malan in Mandarin Chinese.
At a T-junction in the town, soldiers were planting poplar trees along the only main road in and out of the heavily fenced complex. The closer one got to the entrance, the higher the trees grew.
Malan was built in the 1950s in the Bayinguoleng Mongol autonomous prefecture of the Gobi desert. At 472,472 square kilometers, the prefecture is bigger than the United Kingdom, and the testing site, about 200 km from the base, covers an area of 100,000 sq km, almost equal in size to Jiangsu province.
Its remote location meant Malan was one of the world's best sites for nuclear tests. An added advantage was that much of the radioactive material released by the bombs, which were detonated in mid-air, was captured in the soil of a dried out, funnel-shaped lake called Lop Nur, where it could later be easily collected for examination.
On July 29, 1996, China conducted its last nuclear test. On the same day, the government announced that all nuclear tests would cease as of July 30. After that, Malan's role began to change, but the base was still a highly classified secret.
About 35 km from the base next to Wushitala, Malan's nuclear research center is hidden deep in the Tianshan mountains. Locals say that during the summer horse orchids cover the mountains in a blaze of color.
In 1986, China announced that it would not carry out tests in the atmosphere because of the dangers of radioactive pollution. The Malan center was then abandoned and the members of the research team moved to Xi'an, capital of Shaanxi province.
Flash floods have destroyed many sections of the narrow rugged road to the former research center, although many old military checkpoints still remain as a reminder of the days when the area was a highly restricted military zone.

 Michelle lays roses at site along Berlin Wall
Michelle lays roses at site along Berlin Wall
 Historic space lecture in Tiangong-1 commences
Historic space lecture in Tiangong-1 commences
 'Sopranos' Star James Gandolfini dead at 51
'Sopranos' Star James Gandolfini dead at 51
 UN: Number of refugees hits 18-year high
UN: Number of refugees hits 18-year high
 Slide: Jet exercises from aircraft carrier
Slide: Jet exercises from aircraft carrier
 Talks establish fishery hotline
Talks establish fishery hotline
 Foreign buyers eye Chinese drones
Foreign buyers eye Chinese drones
 UN chief hails China's peacekeepers
UN chief hails China's peacekeepers
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
Shenzhou X astronaut gives lecture today
US told to reassess duties on Chinese paper
Chinese seek greater share of satellite market
Russia rejects Obama's nuke cut proposal
US immigration bill sees Senate breakthrough
Brazilian cities revoke fare hikes
Moody's warns on China's local govt debt
Air quality in major cities drops in May
US Weekly

|

|