Resurgence of nationalistic sentiment
Updated: 2013-05-22 03:26
By Cai Hong (China Daily)
|
||||||||
Osaka Mayor Toru Hashimoto is said to have a big mouth comparable to Shintaro Ishihara, co-leader of the Japan Restoration Party. Hashimoto's critics have named the rabble-rouser's style "Hashism", a combination of "Hashimoto" and "fascism".
Even after falling public support for his party following his recent controversial remarks on "comfort women" (World War II-era sex slaves of the Japanese military) and the present-day "adult entertainment industry" (the sex trade), Hashimoto has not retracted his statements.
 |
|
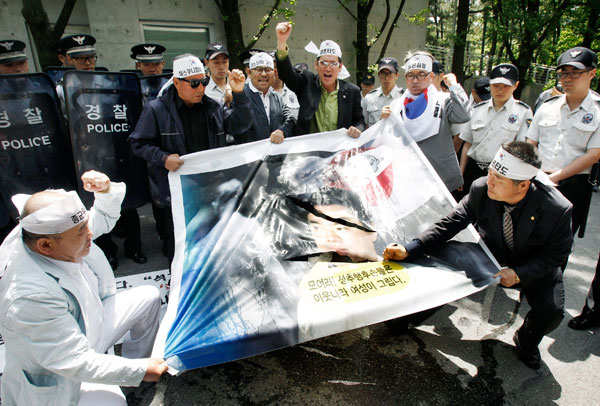
A South Korean protester uses a knife to tear a portrait of Osaka Mayor Toru Hashimoto during a rally against Japan in front of the Japanese ambassador's residence in Seoul on Tuesday. Ahn Young-joon / Associated Press |
"Even though I have repeatedly said that I didn't think the comfort women system was necessary, (an opinion poll) is ... based on the premise that I believe the comfort women system was necessary," Hashimoto told his supporters in Sakai city, Osaka, on Monday.
He insisted that allowing troops to have a sexual outlet was necessary. "Japan's comfort women system was wrong. However, militaries in other countries used women. Nevertheless, the world only criticizes Japan as it used 'sex slaves'," he said.
Seventy-one percent of the respondents in a survey by the Mainichi Shimbun newspaper and 75 percent of the interviewees in a survey by the Asahi Shimbun newspaper over the weekend did not share Hashimoto's opinion.
Hashimoto did not make a slip of the tongue, but showed his perception of history.
His past comments betray his notoriety and cater to far-right sentiments.
Before becoming Osaka governor in 2008, Hashimoto argued on several television programs that Japan should have nuclear weapons.
"What's needed in the politics of today's Japan is a dictator - power to the extent you'll be called a dictator," Hashimoto said in 2011. This comment made national and international headlines. Critics warn that he is the most dangerous man in Japan.
This time he has hit rock bottom, so he rented some drilling equipment. He claimed that he may have lacked "international sensitivity". Hashimoto said on Thursday that his comments were not intended to justify or whitewash Japan's use of prostitution for its wartime military and that Japan should apologize to the women whether or not they were forced into it.
Historians say that as many as 200,000 women, mainly from the Korean Peninsula and China, were forced to provide sex for Japanese soldiers in military brothels during World War II.
Hashimoto is a telling clue of a resurgence of nationalistic sentiment in Japan.
Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe is a nationalist politician with a decade-long track record of attempts to revise or downplay Japan's history of militarism and imperialism.
On April 25, Abe questioned the aggressive character of Japan's World War II colonialism when he announced a revision of Japan's official 1995 apology for its wartime aggression. Abe claimed that the definition of "aggression", used to describe the country's World War II policies in Asia, was hard to establish.
"The definition of what constitutes an invasion has yet to be established in academia or in the international community," Abe said in the Japanese parliament. "Things that happened between nations will look different depending on which side you view them from."
By any standard, Japan adopted a policy of aggression in the 1930s and 1940s in large parts of Asia. In denial of universally acknowledged historical facts, the ruling Liberal Democratic Party policymakers and lawmakers have regularly claimed that Japanese imperialism and colonialism should not be referred to as such. Instead, they argue that Japan conducted a war that liberated Asia from Western colonial powers at the time.
"My ministers will not yield to any kind of intimidation," Abe said in Parliament after visits to the controversial Yasukuni Shrine on April 20 and 21 by three Cabinet ministers, including Deputy Prime Minister Taro Aso, and another 168 Japanese lawmakers on April 23. The Yasukuni Shrine honors Japan's war dead, including 14 "Class A" war criminals.

 Michelle lays roses at site along Berlin Wall
Michelle lays roses at site along Berlin Wall
 Historic space lecture in Tiangong-1 commences
Historic space lecture in Tiangong-1 commences
 'Sopranos' Star James Gandolfini dead at 51
'Sopranos' Star James Gandolfini dead at 51
 UN: Number of refugees hits 18-year high
UN: Number of refugees hits 18-year high
 Slide: Jet exercises from aircraft carrier
Slide: Jet exercises from aircraft carrier
 Talks establish fishery hotline
Talks establish fishery hotline
 Foreign buyers eye Chinese drones
Foreign buyers eye Chinese drones
 UN chief hails China's peacekeepers
UN chief hails China's peacekeepers
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
Shenzhou X astronaut gives lecture today
US told to reassess duties on Chinese paper
Chinese seek greater share of satellite market
Russia rejects Obama's nuke cut proposal
US immigration bill sees Senate breakthrough
Brazilian cities revoke fare hikes
Moody's warns on China's local govt debt
Air quality in major cities drops in May
US Weekly

|

|