Eating event adds spice to GM food debate
Updated: 2013-10-23 07:10
By Zhang Lei and Zhong Nan in Beijing (China Daily USA)
|
||||||||
Public caught up in argument over safety of genetically modified products, report Zhang Lei and Zhong Nan in Beijing.
More than 300 people gathered to enjoy a bowl of porridge made from genetically modified food on Saturday, an attempt to quell public fears about the safety of the product.
The first China Golden Rice Tasting Event was held at Huazhong Agricultural University in Wuhan, Hubei province, sparking another round in the nationwide debate about the safety of GM crops, often called "Frankenfood" by opponents.
Similar events have been held in more than 28 cities since May, the university said.
Both the pro and anti camps have posted conflicting comments on the Internet, with each providing evidence to back up their beliefs, but the exchanges are becoming increasingly bitter.
Jiang Tao, a senior engineer at the Center for Agricultural Resources Research at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, who is in favor of GM foods, was scathing about what he called "amateurs" spreading rumors.
"Just look at the people who are opposed to GM foods; can you find anyone from a related field in the scientific community?" he asked. Jiang also accused the anti-GM lobby of repeatedly using outdated or inaccurate data to support an "incorrect" stance.
Chen Yunfa, an independent researcher into the Yangtze River Delta economy, recently wrote a commentary on the Internet news portal Eastday in which he denounced the actions of the 61 scientists, saying they had gone "beyond their proper duty". He suggested that large multinational corporations might be behind the letter and similar incidents, prompted by a desire to freeze China's patent hybrid rice technology out of the market.
To support his contentions, Chen said that GM rice, first produced by scientists in the US, still hasn't gained official approval from the US government. However, the US authorities have actually granted licenses to six varieties of GM rice. The commercial planting of two varieties - anti-herbicide (BAR) transgenic rice LL RICE 06 and LL RICE 62 - produced by the French pharmaceutical company Sanofi-Aventis, was approved in 1999 and a license for cultivation for edible use was granted in 2000.
Limited land resources
Earlier this month, Max Holtzman, senior advisor to the United States Secretary of Agriculture, told China National Radio that more than 90 percent of US-produced corn and soybeans are GM crops. He said that 20 percent of the corn and 40 percent of soybeans are exported, while the remainder is consumed domestically. Approximately 70 percent of all processed foods in the US market contain genetically modified ingredients and, to date, there has never been a safety incident associated with the consumption of GM foods, he added.
One of the 61 petitioners, Zhang Qifa, director of the National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement at Huazhong Agriculture University, said delaying the commercial cultivation of GM rice would cause great harm to China and science. His comments echoed a statement by the scientists, who criticized the Ministry of Agriculture for dragging its feet over the issue.
"When two of our GM rice varieties were granted safety certificates by the Ministry of Agriculture in 2009, I was quite confident. But four years later, the ministry still hasn't rolled out any specific protocols for the commercialization of GM rice," said Zhang.
Currently, the safety certificates issued to Zhang's research team are the only ones to have been awarded in China, and he fears that the commercialization of GM rice in China is unlikely to make much headway once they expire in May next year.
Lin Yongjun, project leader of insect-resistant transgenic rice varieties at Huazhong Agricultural University, said the certificates were granted only after rigorous testing and inspection, including a 90-day experiment during which the rice was fed to rats, and tests carried out on three successive generations of rice to ensure product safety.
Zhang said the urgent need for the commercialization of GM foods corresponds to calls from academics keen to correct the imbalance between China's grain output and demand. Wu Kongming, an academician at the Chinese Academy of Engineering, said the situation is so grave that China cannot afford to postpone the development and adoption of GM technology.
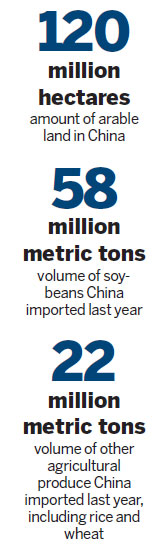
"China has 1.8 billion mu (120 million hectares) of arable land. The country imported more than 58 million metric tons of soybeans last year, and if rice, wheat, barley and canola are also included, imports totaled 80 million tons. It would take 800 million mu just to plant an equal amount of food. China is not rich in land resources, so we can't simply rely on traditional methods to meet our requirements. We must take advantage of modern high-tech agriculture," he said.
GM crops have a number of obvious advantages, including high yield rates and increased resistance to pests, which could result in more efficient use of land and a reduction in the use of pesticides. Cultivation of GM cotton and papaya has already been approved, but because those crops don't belong to the mainstream food groups, there has been less resistance to their use.
Rice, however, is a different matter because it is the staple food of most Chinese people. Although experts have emphasized that the State has issued safety certificates for two varieties of GM rice, many people still harbor doubts about its safety. Lin believes there is a crisis of public confidence and said that, given the number of food scandals in the country in recent years, many people are skeptical of safety claims.
Public doubt concerning the safety of GM foods was highlighted when Internet users overwhelmingly sided with Cui Yongyuan, a presenter at China Central Television, who engaged in an online spat with a proponent of modified foods last month.
Cui took exception to claims made by a well-known micro blog opinion leader, Fang Zhouzi, about the safety of GM foods. When Fang posted on Weibo, China's version of Twitter, that every Chinese should be granted the opportunity to eat GM foods, Cui was quick to respond, saying that he reserved the right to not eat GM foods and to question the science Fang proclaimed.
While acknowledging Cui's right not to eat GM foods, Fang pointed out that "science is science", and said the dissemination of unfounded rumors will hinder the development of agriculture in China.
'Better safe than sorry'
Another reason behind the public distrust of GM foods is the lack of an effective supervision and management system or transparency of information, according to Zheng Yujie, a researcher at the Industry Research Center of CIConsulting in Shenzhen. "Although in some other countries, people also have questioned the use of GM foods, the public attitude (in those countries) is generally calm," he said.
The dilemma was highlighted in August 2012, when a group of children from Hunan province, ranging from 6 to 8 years old, were fed "golden" rice as part of an experiment. Crucially however, the researchers failed to obtain the consent of the children's guardians.
The parents were outraged, despite the researchers' insistence that GM rice is rich in beta carotene, a pigment known to be beneficial to eyesight and the immune system, which helps prevent vitamin A deficiency in children.
The incident hampered public recognition of GM foods, even though no proof that GM rice is unsafe has been published. "Because of such incidents, people inevitably have increasing doubts, even in the face of scientific fact. There is poor supervision of the labeling of GM foods, but even when the products are properly labeled, many people tend to avoid them, because of a 'better safe than sorry' mentality," said Lin.
He expressed the hope that an independent third party or the Ministry of Agriculture will conduct experiments and make the results public to dispel some of the public disquiet. One of the most-widespread rumors about GM foods, that they can cause cancer and sterility, was officially denied by the Ministry of Agriculture, which issued a wide range of evidence to back its claims, on Oct 17. Lin described the government's move as "a good start".
As China has already permitted import of five types of GM products - soybeans, corn, oilseed rape, cotton and beets - Jiang Tao called on the public to overcome the fear of genetic modifications. "I, for one, oppose the concept of 'pure and natural'. It's an absurd concept and only means something in aesthetics. In all other areas, it is meaningless," he said.
"We humans actually cannot directly eat pure, natural food, because the vast majority of natural fruits have their own self-protection mechanisms, such as toxins or thorns. The food we humans can eat has evolved simultaneously with us. We have changed the original form of our food for thousands of years now. "
Contact the writers at zhanglei@chinadaily.com.cn and zhongnan@chinadaily.com.cn
|
A consumer chooses oil made from non-genetically modified sunflower seeds in a supermarket in Beijing on Tuesday. Feng Yongbin / China Daily |
|
GM rice on display at the first China Golden Rice Tasting Event, held at Huazhong Agricultural University in Wuhan, Hubei province, on Oct 19. Sun Tao for China Daily |

(China Daily USA 10/23/2013 page7)
 Pumpkin fun ahead of Halloween
Pumpkin fun ahead of Halloween
 Weakening Raymond soaks Mexico, no serious damage
Weakening Raymond soaks Mexico, no serious damage Apple unveils new Macs, iPad ahead of holidays
Apple unveils new Macs, iPad ahead of holidays
 Smart cities to aid urbanization
Smart cities to aid urbanization
 In control & breaking the mold
In control & breaking the mold
 Higher retirement age may help solve pension problem
Higher retirement age may help solve pension problem
 Northeast remains shrouded in smog for third straight day
Northeast remains shrouded in smog for third straight day
 Beijing Opera troupe perform in Brazil
Beijing Opera troupe perform in Brazil
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks
|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
NASA: Chinese scientists are now welcome
Yingli uses US baseball stars in campaign
Top officials promote new relations
China's US Treasury holdings hit six-month low
Graduate looks at kung fu-hip hop connection
Apple unveils new Macs, iPad
San Francisco train service restarts after strike
China, Russia reach big oil deal
US Weekly

|

|